25, 2018. It aims to give individuals more control over their personal data and to harmonize data privacy laws across Europe. This article will delve into the key aspects of GDPR, its implications for businesses, and how organizations can ensure compliance.
What is GDPR?
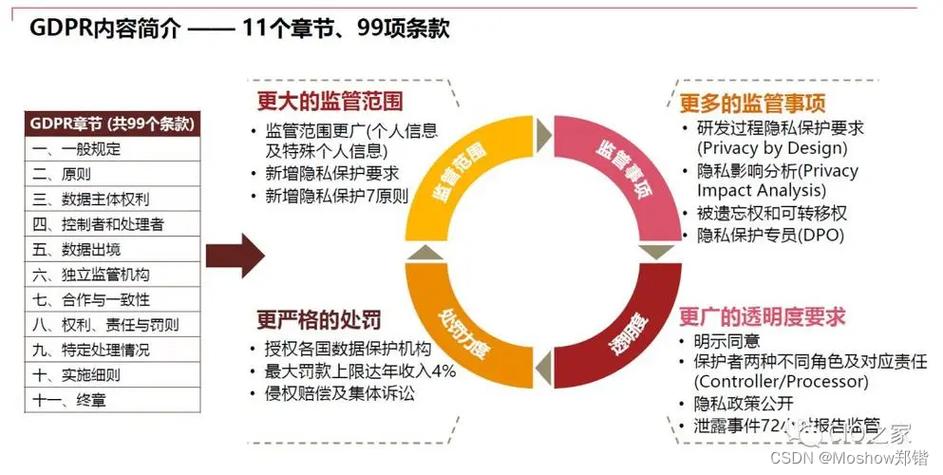
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a regulation in EU law on data protection and privacy for all individuals within the European Union and the European Economic Area (EEA). It also addresses the export of personal data outside the EU and EEA areas. GDPR aims to give control back to citizens and residents over their personal data and to simplify the regulatory environment for international business by unifying the regulation within the EU.
Key Principles of GDPR
Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
GDPR requires that personal data be processed lawfully, fairly, and in a transparent manner. This means that organizations must have a legitimate reason for processing personal data and must inform individuals about how their data will be used.
Purpose Limitation
Personal data should be collected for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes and not further processed in a manner that is incompatible with those purposes. Organizations must clearly define the purpose of data collection and ensure that data is not used for unrelated activities.
Data Minimization
Organizations should only collect data that is necessary for the purposes for which it is being processed. This principle ensures that the amount of personal data collected is limited to what is directly relevant and necessary.
Accuracy
Personal data must be accurate and, where necessary, kept up to date. Organizations must take every reasonable step to ensure that inaccurate data is erased or rectified without delay.
Storage Limitation
Personal data should be kept in a form that permits identification of data subjects for no longer than is necessary for the purposes for which the data is processed. Organizations must establish and adhere to data retention policies.
Integrity and Confidentiality
Personal data must be processed in a manner that ensures appropriate security, including protection against unauthorized or unlawful processing and against accidental loss, destruction, or damage. Organizations must implement technical and organizational measures to safeguard data.
Implications for Businesses
GDPR has significant implications for businesses, regardless of their size or location. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, which can be up to 4% of annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is greater. Here are some key areas businesses need to focus on:
Data Protection Officers (DPOs)
Certain organizations are required to appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to oversee GDPR compliance. The DPO is responsible for monitoring internal compliance, advising on data protection obligations, and acting as a point of contact for supervisory authorities and data subjects.
Data Breach Notifications
GDPR mandates that organizations report data breaches to the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours of becoming aware of the breach. In cases where the breach is likely to result in a high risk to the rights and freedoms of individuals, the affected data subjects must also be informed without undue delay.
Consent
Consent must be freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous. Organizations must ensure that they obtain explicit consent from individuals before processing their personal data. Pre-ticked boxes or implied consent are no longer acceptable under GDPR.
Data Subject Rights
GDPR grants several rights to data subjects, including the right to access, rectify, erase, restrict processing, and object to the processing of their personal data. Organizations must have processes in place to respond to data subject requests within the stipulated timeframes.
Ensuring GDPR Compliance
Ensuring GDPR compliance requires a comprehensive approach that involves legal, technical, and organizational measures. Here are some steps organizations can take:
Conduct a Data Audit
Organizations should start by conducting a thorough data audit to understand what personal data they hold, where it is stored, how it is processed, and who has access to it. This will help identify any gaps in compliance and areas that need improvement.
Implement Data Protection Measures
Organizations must implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data. This includes encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments.
Develop a Data Protection Policy
A comprehensive data protection policy should be developed and communicated to all employees. This policy should outline the organization's approach to data protection, including roles and responsibilities, data handling procedures, and incident response plans.
Train Employees
Employees play a crucial role in ensuring GDPR compliance. Regular training should be provided to ensure that employees understand their data protection obligations and how to handle personal data in accordance with GDPR requirements.
Monitor and Review Compliance
GDPR compliance is an ongoing process. Organizations should regularly monitor and review their data protection practices to ensure continued compliance and to address any emerging risks or challenges.
In conclusion, GDPR is a landmark regulation that has reshaped the data protection landscape. Organizations must take proactive steps to ensure compliance and protect the personal data of individuals. By understanding the key principles of GDPR, addressing its implications, and implementing robust data protection measures, businesses can not only avoid hefty fines but also build trust with their customers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is GDPR?
GDPR stands for General Data Protection Regulation, a comprehensive data protection law in the EU that gives individuals more control over their personal data and simplifies the regulatory environment for international business.
Who does GDPR apply to?
GDPR applies to all organizations that process personal data of individuals within the EU, regardless of where the organization is located.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with GDPR?
Non-compliance with GDPR can result in fines of up to 4% of annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is greater.
What are the key principles of GDPR?
The key principles of GDPR include lawfulness, fairness, and transparency; purpose limitation; data minimization; accuracy; storage limitation; and integrity and confidentiality.


